Synonym TyraminEffekt 1 Definition CheeseEffekt bezeichnet das Auftreten einer hypertensiven Krise durch gleichzeitige Einnahme von MAOHemmern und tyraminreichen Nahrungsmitteln (zB Rotwein, Käse)Tyramin entsteht bei der Zersetzung von Eiweißen aus der Aminosäure Tyrosin und ist enthalten in Nahrungsmitteln, zu deren Fertigung Schritte wie Gärung oder Fermentation gehören, so z B viele Käsesorten, Rotweine oder Schokolade Es ist des Weiteren Inhaltsstoff von Bananen und Misteln – in den Beeren letzterer sogar in giftiger Konzentration · So while you are taking MAOIs for depression, Dr Edlund explains, your body is already working harder to process naturally occurring tyramine Any tyramine that comes from your diet is "extra," and can easily accumulate in your body and overload the system That's what causes side effects such as headaches and elevated blood pressure, as well as gastrointestinal upset, rapid heartbeat, shortness in breath, and neurological problems like confusion, anxiety, and vision

Pdf Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Dietary Tyramine And Drug Interactions
Interaction between tyramine and maoi
Interaction between tyramine and maoi-Monoamine oxidase inhibitors and the cheese effect The behavior of inhibitors of monoamine oxidaseA (MAOA) is considered in terms of the possibility of having an effective antidepressant that does not give rise to hypertensive interactions with dietary tyramineThus, selective inhibition of MAO A, or inhibition of both isoforms, will cause tyramine potentiation (cheese effect), which originate a thumping heartbreak and a progressive increase in blood



Maoi Side Effects Page 1 Line 17qq Com
If the patient is taking a MOA inhibitor, Tyramine accumulates in the bloodstream;Examples of foods high in tyramine include Strong or aged cheeses, such as aged cheddar, Swiss and Parmesan; · An acute attack of hypertension that can occur in a person taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) drug who eats cheese, caused by an interaction of the MAOI with tyramine, formed in ripe cheese when bacteria provide an enzyme that reacts with the amino acid tyrosine in the cheese Other foods and drinks that produce the same effect include pickled
Elevated tyramine can cause your blood vessels to narrow, possibly leading to critically high blood pressure 4 You will need to avoid foods high in tyramine while you are taking an MAOI 5 You will also need to continue to avoid them for 2–4 weeks after you stop taking an MAOIAnother aspect of the pharmacology of MAOI which I found interesting was the potentiation of the indirect 1 3 sympathomimetic effect of tyramine (a monoamine which occurs in yellow cheese) by MAOITyramine is a natural compound found in plants and animals It is a byproduct of the breakdown of tyrosine, an amino acid Tyrosine and tyramine
It has indirect sympathomimetic action causing the release of stored catecholamines This is known as the "Cheese effect"!!!チラミン(Tyramine;4hydroxy phenylethylamine,C 8 H 11 NO)は、生体内で芳香族Lアミノ酸デカルボキシラーゼの作用によりチロシン(Tyr)から産生されるアミンで、フェネチルアミンの誘導体の1つである。 チラミンは、モノアミン神経伝達物質(セロトニン、ノルアドレナリン、アドレナリン、ヒスBlocking this enzyme helps relieve depression If you take an MAOI and you eat hightyramine foods, tyramine can quickly reach dangerous levels This can cause a serious spike in blood pressure and require emergency treatment Avoid consuming foods that are high in tyramine if



Cheese Reaction Mechanism Mao Inhibitors Tyramine Drug Interactions Pharmacology Made Easy Youtube



Low Tyramine Diet Foods High In Tyramine May Cause Serious Effects When Combined With Certain Medications Patient Education Pdf Free Download
One was liver toxicity, the other as the "cheese effect", which was caused by tyramine Many foodstuffs such as cheese (but also including other fermented products like draught beer, wine, pizza and yeast products like Marmite) contain significant levels of tyramine, which causes release of noradrenaline Subsequently high levels of tyramineThe rule of thumb for cheeses is the softer, the older, and the smellier, the higher the tyramine content Any food whose taste is produced by fermentation should be assessed carefully Be careful with leftovers For more information on tyramine restricted foods go to the Grossi's recommended links from the home page of this site This reaction is the socalled cheese effect or tyramine effectMeats, Dairy Products and Fruits and Vegetables ;



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Pdf Pharmacology Of Mao B Inhibitors And The Cheese Reaction
· The behavior of inhibitors of monoamine oxidaseA (MAOA) is considered in terms of the possibility of having an effective antidepressant that does not give rise to hypertensive interactions with dietary tyramine Studies with punchbiopsy samples of human intestine and rat intestinal samples show MAOA to be the predominant form of the enzyme in both speciesMan spricht dann vom sogenannten „CheeseEffect" Tyramin ist ein unspezifisches Substrat der Monoaminooxidasen Des Weiteren kann Tyramin wie andere biogene Amine (u a Histamin in Erdbeeren, in Schalen und Krustentieren;And Cured meats, which are meats treated with salt and nitrate or nitrite, such as drytype summer sausages, pepperoni and SmokedAny fermented dairy products, like cheese, sour cream, processed cheese, buttermilk,


Pdf Hypertensive Crisis And Cheese



Pdf Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors A Review Concerning Dietary Tyramine And Drug Interactions
Written by Esther Kinuthia RN BSN BA 08 July, 11 Fact Checked Monoamine oxidase inhibitors areFrom Infogalactic the planetary knowledge core Jump to navigation, search Tyramine;We present a safe and practical MAOI diet based on the related clinical and analytic data METHOD We used a critical review of the literature and our own tyramine assay results to categorize foods to be restricted absolutely, taken in moderation only, or unrestricted RESULTS We recommend that users avoid aged cheese;



Maoi



Tyramine Food Examples Page 2 Line 17qq Com
Posted in Brain Health Hey guys, been reading for a long time but never planned to create an account til now I've been taking Rhodiola Rosea 3% extract for about 2 weeks and was having a great experience until 2 days ago I read a few cases of it acting as a weak MAOI but most people say its nothing to be concerned aboutPotentiation of the cardiovascular and other effects of dietary tyramine by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (cheese effect) has been a major limitation to clinical use of these drugs The discovery that MAO exists in two distinct isoforms, MAOA and MAOB, together with the development of selective inhibitors of each isoform, enabled the understanding that selective · Tyramine causes hypertensive crises after MAO inhibition aka the "cheese effect" or "cheese crisis" Using a MAO inhibitor (MAOI), the intake of approximately 10 to 25 mg of tyramine is required for a severe reaction compared to 6 to 10 mg for a mild reaction Tyramine rich food should also be avoided by people prone to headache and migraine



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download
A "cheese reaction"or the "cheese effect" 2,3 This is because in the early days of MAOI use, it was noticed that some people experienced headaches after eating cheese Even today, this is known as the "cheese effect" or "cheese syndrome," but other foods and beverages high in tyramine can also cause the symptoms2 · In Anlehnung an den hohen TyraminGehalt gereiften Käses wird dieses Phänomen als „CheeseEffekt" bezeichnet Im Übrigen ist bei Tyramin anders als bei anderen indirekten SympathomimetikaRetrieved on 0712 "At dosages above around 2 mg per day, rasagiline loses its selectivity for MAO type B and also inhibits MAO type A An MAOB selective regimen does not cause significant tyramine potentiation, the dreaded 'cheese effect' common to users of older unselective and irreversible MAOIs who eat tyraminerich foods Thus low



Pdf Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Dietary Tyramine And Drug Interactions



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library
· Monoamine oxidase also breaks down tyramine, a chemical present in aged cheese, wines, and other aged foods Since MAOIs inhibit monoamine oxidase, they decrease the breakdown of tyramine from ingested food, thus increasing the level of tyramine in the body Excessive tyramine can elevate blood pressure and cause a hypertensive crisis Patients treated1004 · In particular, foods containing tyramine, a naturally occurring amino acid, can cause a hypertensive crisis in some people who are taking MAOIs This is known as the "cheese effect" as there are particularly high concentrations of tyramine in aged cheeseThey were successful but suffered two side effects;



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry



Well Known Side Effects Of Antidepressants You Should Be Aware Of
Paratyramine, mydrial or uteramin) is a naturally occurring monoamine compound and trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosineTyramine acts by inducing the release of catecholamineAn important characteristic of this product is its impediment to cross the bloodbrain barrier which restrains its side effects to only nonpsychoactiveThe tyramine pressor dose (minimum dose of tyramine necessary to achieve endpoint) for Period 1 was established through a series of three tyramine challenges (24 hours apart) with tyramine doses based upon a predetermined paradigm During Period 1, untreated fasting subjects received an initial tyramine challenge dose of 400 mg and were monitored for SBP endpoint changesThe selective monoamine oxidase (MAO) B inhibitor ()deprenyl failed to produce any greater benefit than placebo in a limited doubleblind trial conducted in depressive patients Its relative freedom from the socalled cheese effect was confirmed, however, in drugtreated patients challenged IV with tyramine There is evidence to suggest that this cheese effect, a facilitated tyramine
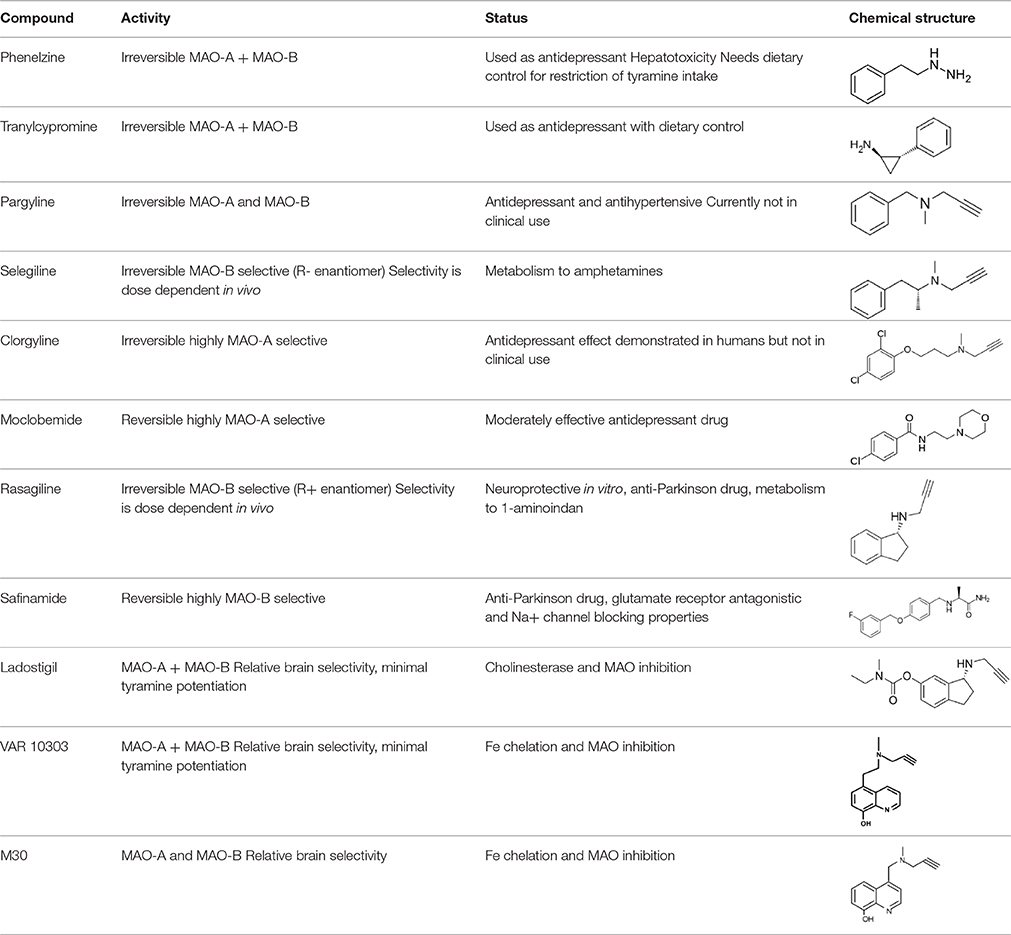


Frontiers Inhibitors Of Mao A And Mao B In Psychiatry And Neurology Pharmacology
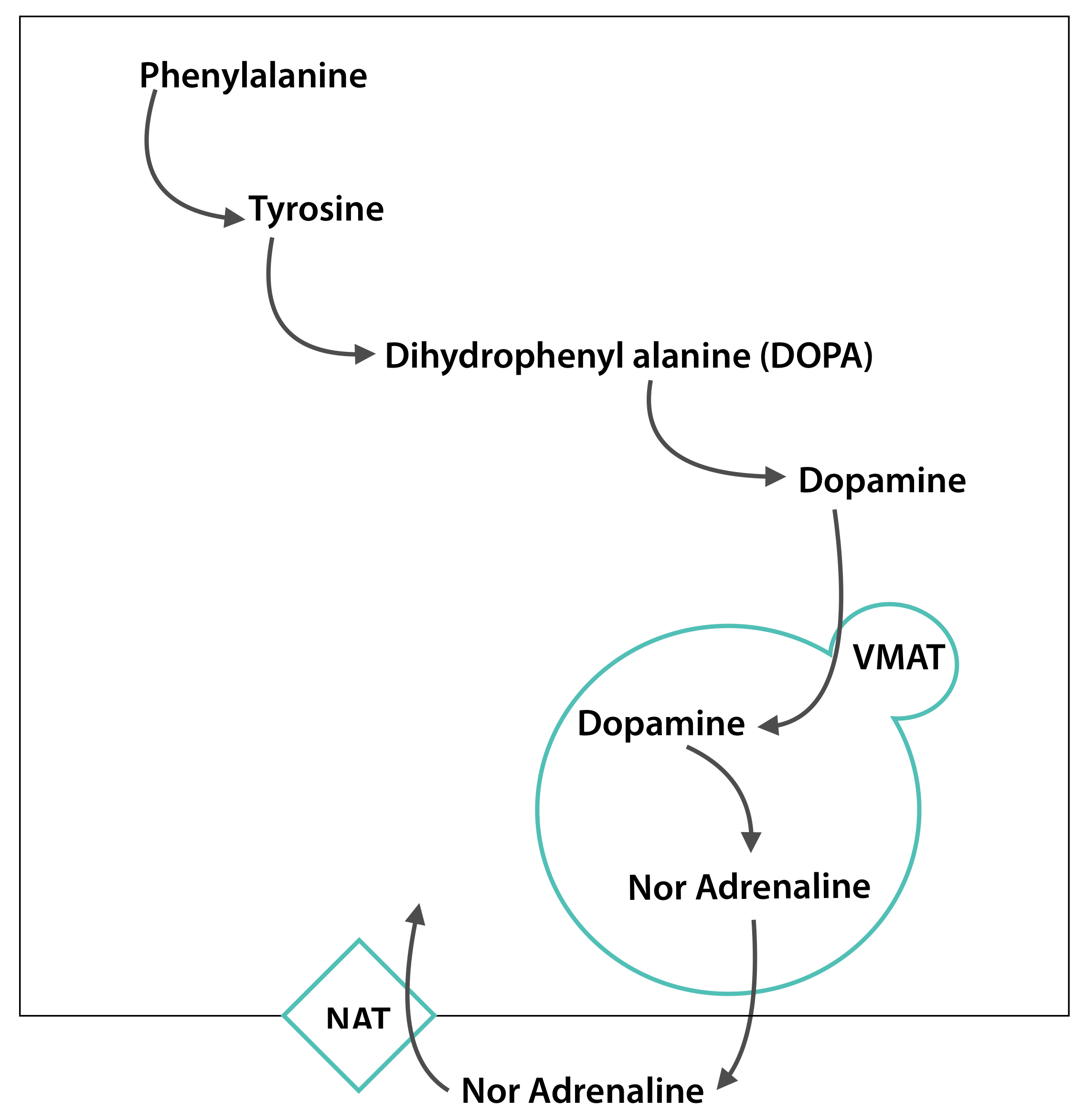


Death By Chocolate The Cheese Reaction Firstclass
· TYRAMINE PRESSOR RESPONSE Pressor Response Patients who are prescribed MAOIs are advised to avoid foods rich in tyramine (eg aged cheeses and red wine) MAOIs inhibit the breakdown of tyramine, which can quickly develop into a hypertensive crisis characterised by severe headache, anxiety, confusion, and palpitations Anderson et al 1993 · Tyramine is a compound produced by the breakdown of an amino acid called tyrosine It's naturally present in some foods, plants, and animals Learn what tyramineMAOIs fell out of favor because of the "cheese effect," which caused lifethreatening headaches in people on MAOIs who ate products that contained cheese The connection was discovered by a British pharmacist who noticed that his wife, who was taking an MAOI, had a severe headache whenever she had a meal with cheese Cheese contains tyramine, a compound found in many



Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants



Tyramine Effect Page 1 Line 17qq Com
· The more food ages, the more concentrated the levels of tyramine become This is true for aged meats, cheeses, and even leftovers in your fridge Foods with dangerously high levels of tyramineWhen ingested unintentionally from certain foods in conjunction with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), tyramine is responsible for the socalled "cheese effect" often seen with their use Occurrence Tyramine occurs widely in plants and animals and is metabolized by the enzyme monoamine oxidase In foods, it is often produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during · Tyramine can also be found in foods especially fermented foods or foods that are close to spoiling This is where the 'cheese effect ' comes into play (Read the background on how it was discovered) A quick list of foods high in tyramine include aged, smoked, or fermented meats (salami, pepperoni, cured sausages, bacon, corned beef, beef



Tyramine Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia



Curcumin And The Mao Inhibitor Cheese Effect From Induced Info
Such a reaction between such foods and MAOIs is called the "cheese effect" Tyramine is a naturally occurring monoamine, which acts as a dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine releasing agent The positive side of MAOIs is that they can show positive results in certain forms of depression where other medications have been ineffective Uses of MAOIs Monoamine oxidaseBlue cheeses such as Stilton and Gorgonzola; · Tyramine is found in aged foods and fermented foods You need to limit the amount of tyramine you eat if you use an MAO inhibitor (MAOI) medicine You can have side effects if you take MAOIs and eat foods that are high in tyramine These side effects include a very bad headache, fast heartbeat, nausea, vomiting, and high blood pressure



Tyramine And Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com



L Tyrosine Benefits Side Effects Dosage Bulksupplements Com
Rhodiola = MAOI, experienced cheese effect!Tyramine (/ˈtaɪrəmiːn/ TYrəmeen) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent Notably, it is unable to cross the bloodbrain barrier, resulting in only nonpsychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion A hypertensiveAlthough we strive to deliver accurate and uptodate information, no guarantee to that effect is made Diseases and Injuries Foods to Avoid When Taking an MAOI Aged Cheese and Matured Cheese ;


Pdf Tyramine In Malt Beverages Interfering With Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Drugs



What Are Mao Inhibitors Healthproadvice
Tyramine is a vasoactive amine that promotes blood pressure elevation, resulting in pain Tyramine leads to cerebral vasoconstriction and subsequent rebound vasodilatation that causes a migraine attack in susceptible persons Episodes can be accompanied by nausea and visual abnormalitiesSerotonin in Bananen und Nüssen) Auslöser für eine Nahrungsmittelallergie sein Darüber hinaus kann der Konsum tyramin und histaminreicherAged or cured meats (eg, airdried sausage);



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology
MAOIs and the cheese reaction B ecause gastrointestinal monoamine oxidase (MAO) effectively prevents dietary pressor amines, typically tyramine, from entering the tissues, a marked hypertensive response (the "cheese reaction") can occur when subjects treated with antidepressant MAO inhibitors ingest foods or beverages rich in such amines · The tyramine interaction ("cheese effect") was first seen in patients treated with an MAOI which inhibits both enzyme forms, particularly tranylcypromine (TCP) or phenelzine Subsequently, drugs were developed which show marked selectivity for one isoform or the other by virtue of their selective binding affinityMonoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of powerful antidepressant drugs prescribed for the treatment of depressionThey are particularly effective in treating atypical depression, and have also shown efficacy in helping people who want to quit smoking Due to potentially lethal dietary and drug interactions, MAOIs had been reserved as a last line of defense, used only when other



The Effect Of Safinamide A Novel Drug For Parkinson S Disease On Pressor Response To Oral Tyramine A Randomized Double Blind Clinical Trial Marquet 12 Clinical Pharmacology Amp Therapeutics Wiley Online Library



Selegiline Wikipedia



What Are Mao Inhibitors Healthproadvice



Talking To Your Patient About Tyramine Youtube



Antidepressants Stahl S Essential Psychopharmacology Neuroscientific Basis And Practical Applications 4th Ed



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Cheese Reactions Tyramine X Mao Inhibitors Pharmacology Easymedicinelearning Youtube



Pdf Determination And Comparison Of The Pressor Effect Of Tyramine During Chronic Moclobemide And Tranylcypromine Treatment In Healthy Volunteers
/GettyImages-746275147-5b0b3813fa6bcc0037205902.jpg)


Dietary Precautions While Taking Maois



Mozzarella Maoi Diet Page 2 Line 17qq Com



Antidepressants Amboss



Cheese Reaction Tyramine Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Maoi Side Effects Page 1 Line 17qq Com
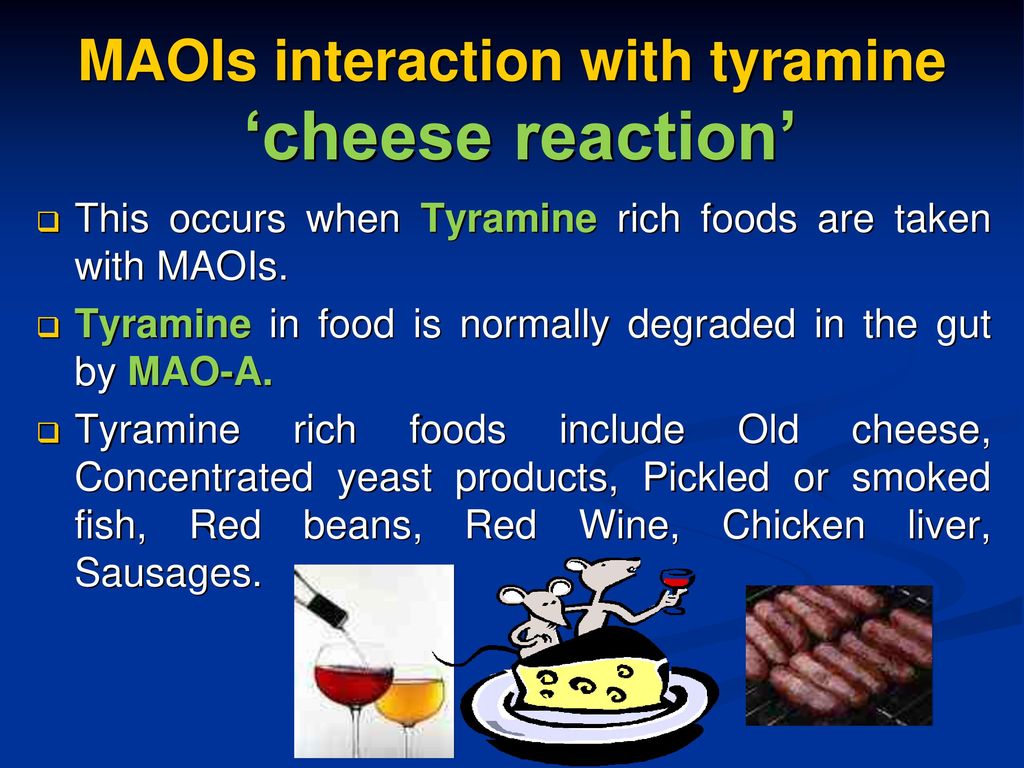


Drugs Used In Depression Prof Yieldez Bassiouni Ppt Download



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library



Pdf Influence Of Food On The Tyramine Pressor Effect During Chronic Moclobemide Treatment Of Healthy Volunteers
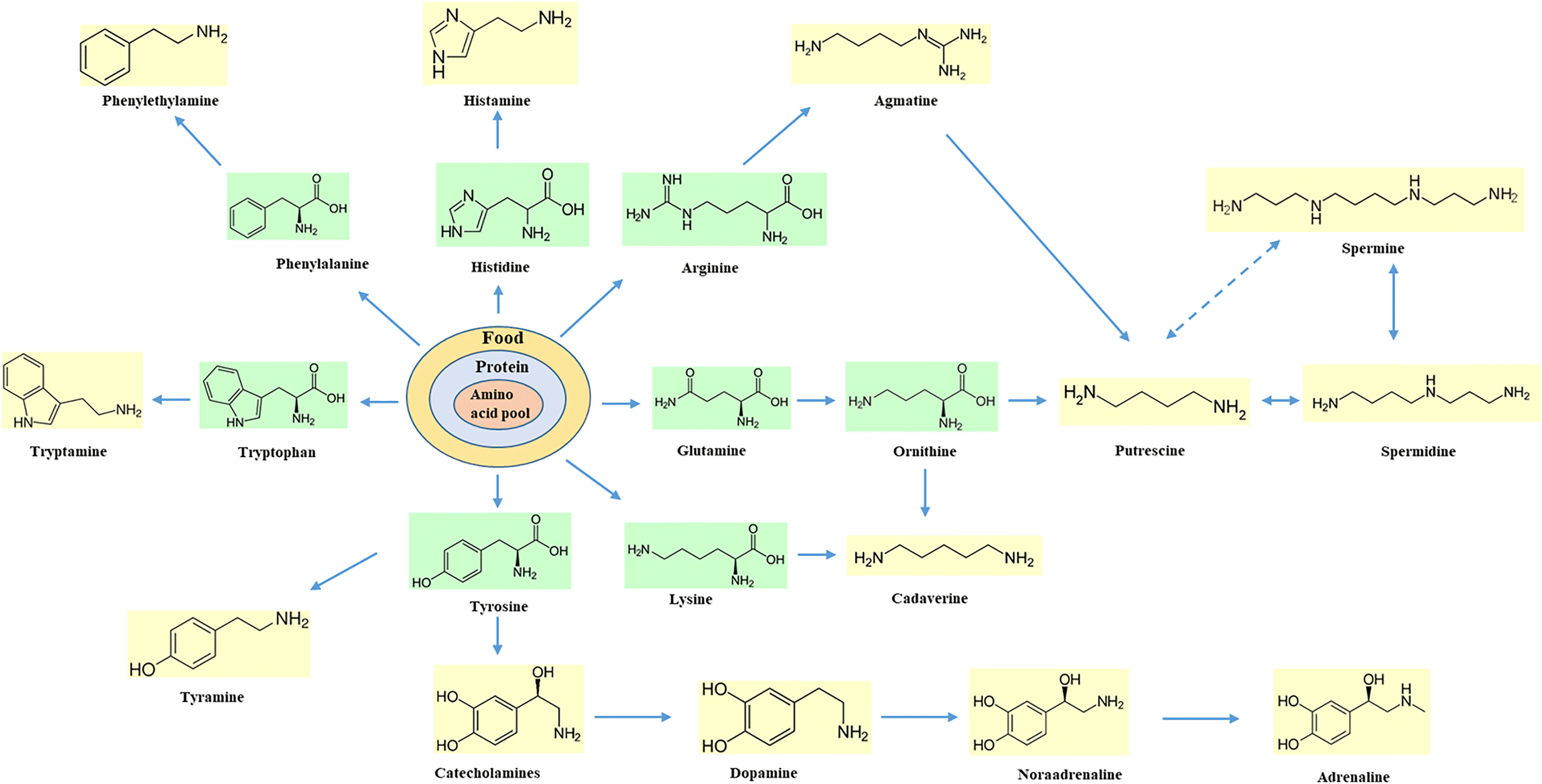


Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039



Tyramine Or Cheese Reaction Hypertensive Crisis Moa Pharmacology Easy Explained Youtube



Tyramine Reaction Page 4 Line 17qq Com



Sembragiline A Novel Selective Monoamine Oxidase Type B Inhibitor For The Treatment Of Alzheimer S Disease Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Osmosis



Tyramine Wikipedia



Pdf Effects Of A Tyramine Enriched Meal On Blood Pressure Response In Healthy Male Volunteers Treated With Selegiline Transdermal System 6 Mg 24 Hour



Prof Elham Aljammas Sept Ppt Download



Maois Diet High Tyramine Foods May Trigger Dangerous Side Effects



Tyramine To Norepinephrine Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Tranylcypromine Wikipedia



Maoi Drugs News



All Foods With Tyramine Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Pdf Oral Tyramine Pressor Test And The Safety Of Mao Inhibitor Drugs



Tyramine Content Low Tyramine Diet Migraines Remedies Maoi Diet



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Comparison Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors In Decreasing Production Of The Autotoxic Dopamine Metabolite 3 4 Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde In Pc12 Cells Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics
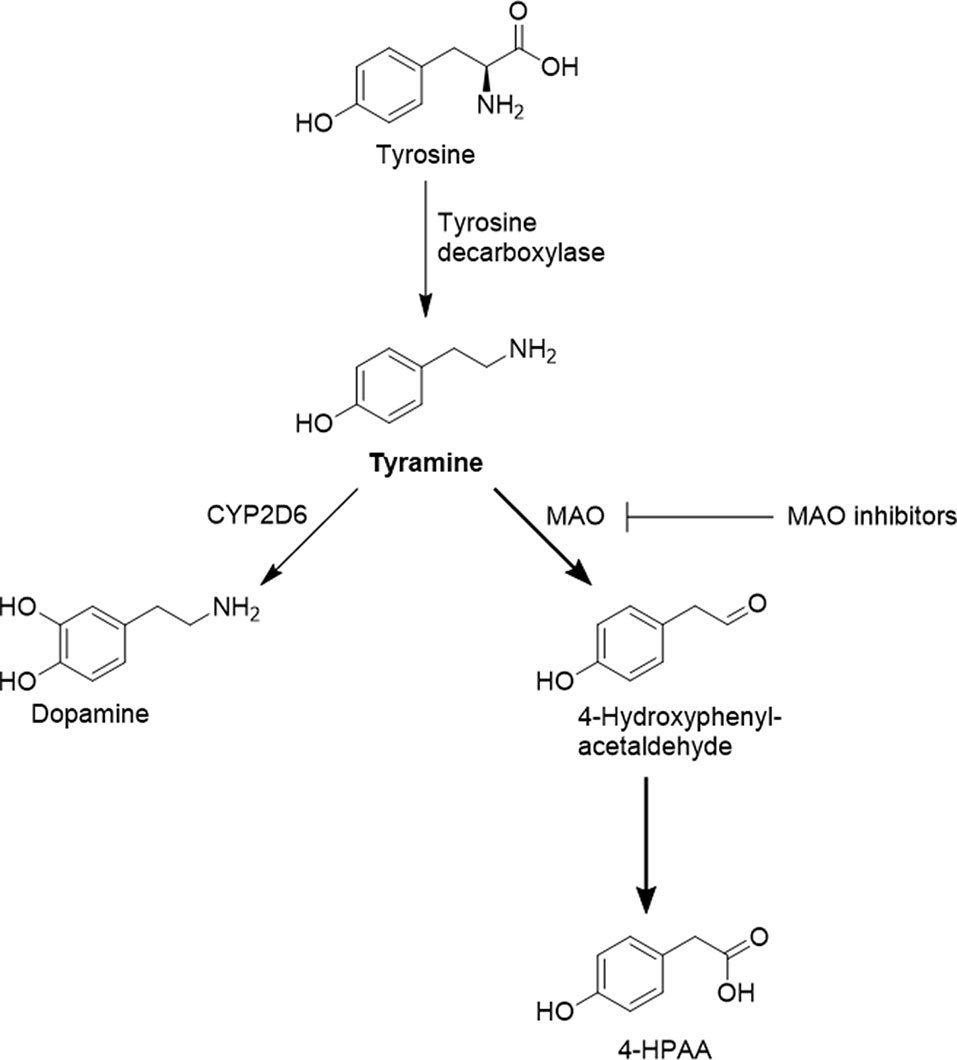


Frontiers Highly Variable Pharmacokinetics Of Tyramine In Humans And Polymorphisms In Oct1 Cyp2d6 And Mao A Pharmacology



Ppt Anti Depressant Medications Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



What Is Cheese Reaction Mao I Non Selective In Pharmacology Youtube



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors A Modern Guide To An Unrequited Class Of Antidepressants Cns Spectrums Cambridge Core



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library
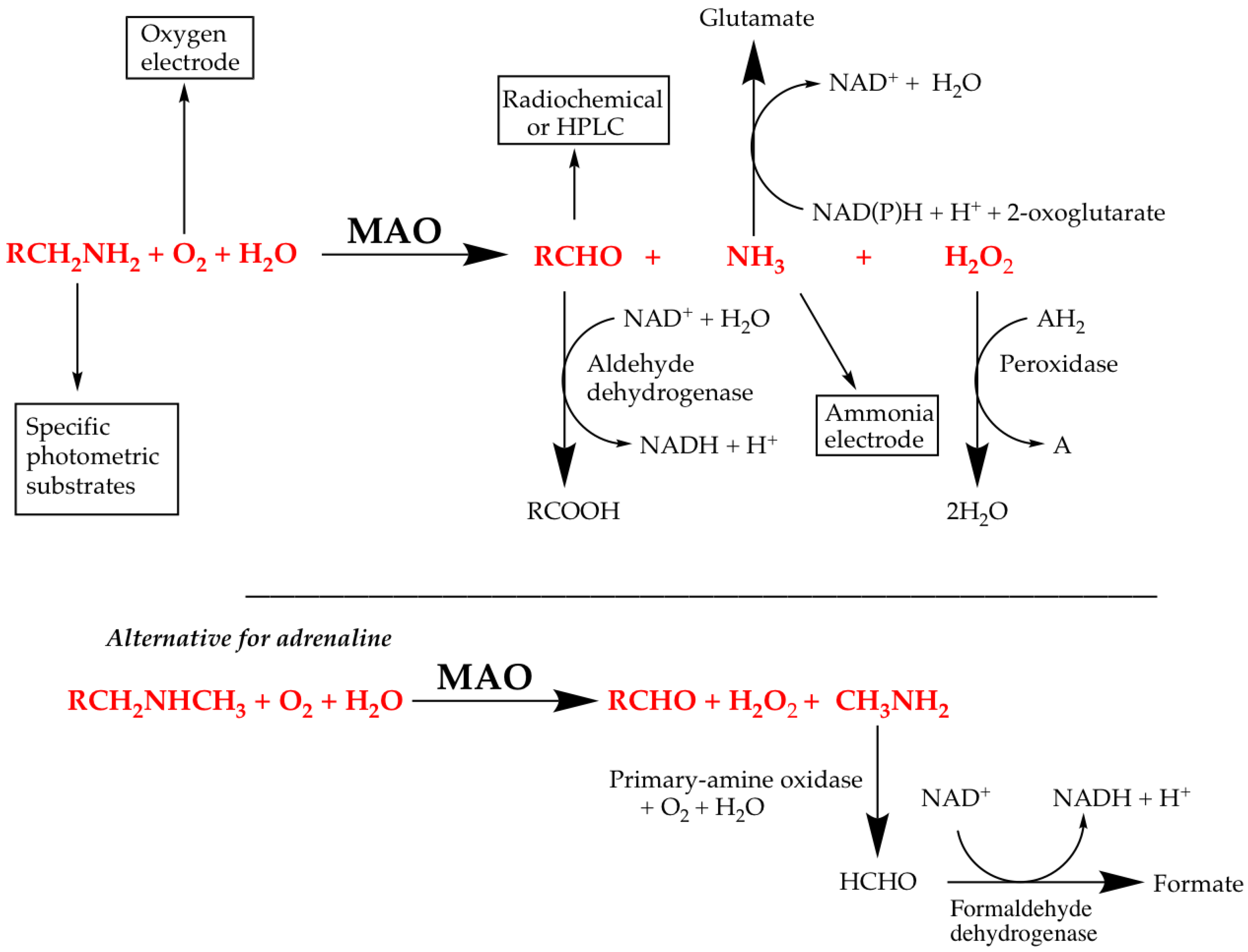


Molecules Free Full Text Assessment Of Enzyme Inhibition A Review With Examples From The Development Of Monoamine Oxidase And Cholinesterase Inhibitory Drugs Html



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology
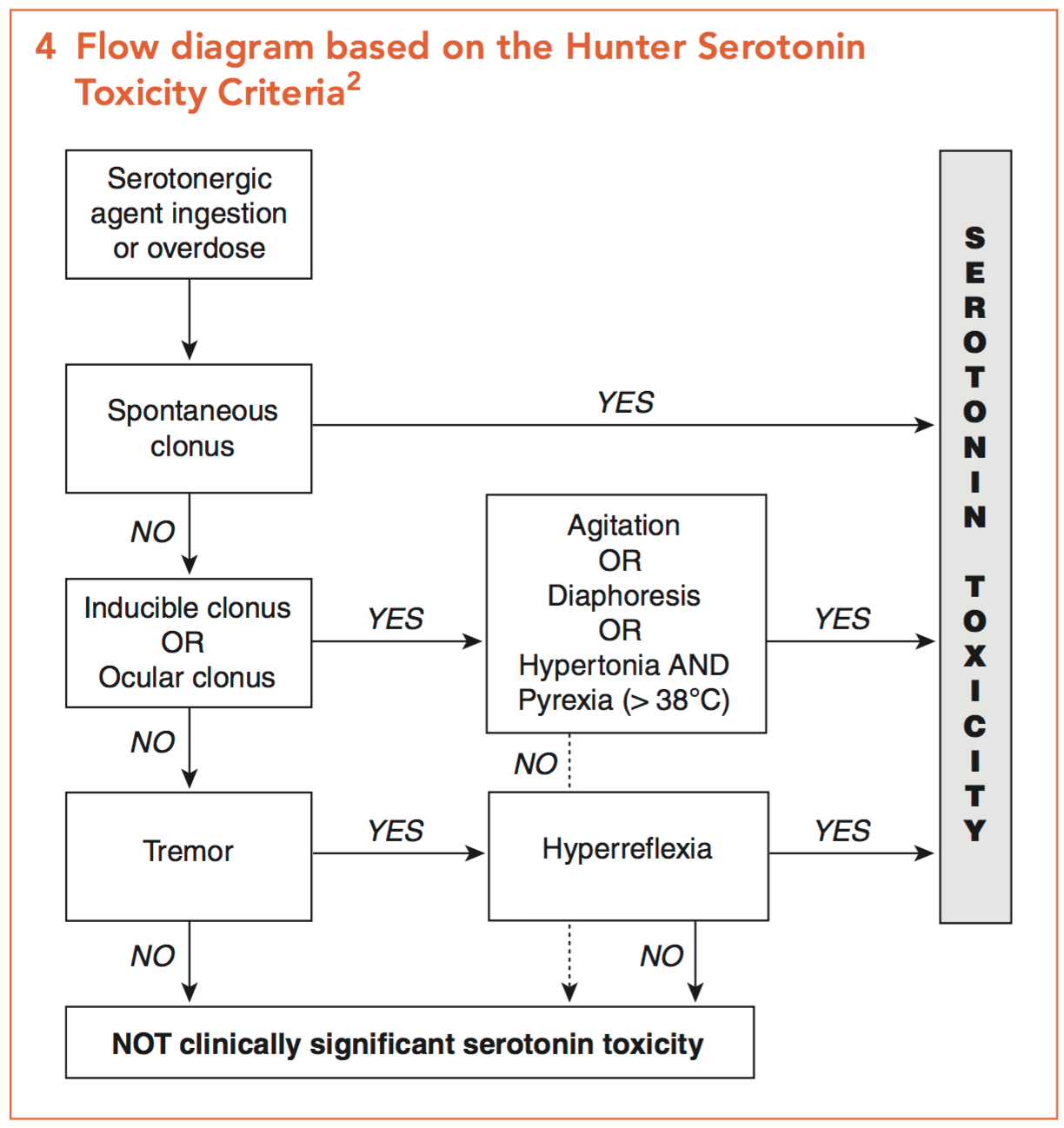


Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants



Pdf Mao Inhibitors Risks Benefits And Lore Semantic Scholar



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry



Cheese Reaction Tyramine Sympathomimetics In Malayalam Youtube



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library



Pdf Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Clinical Review
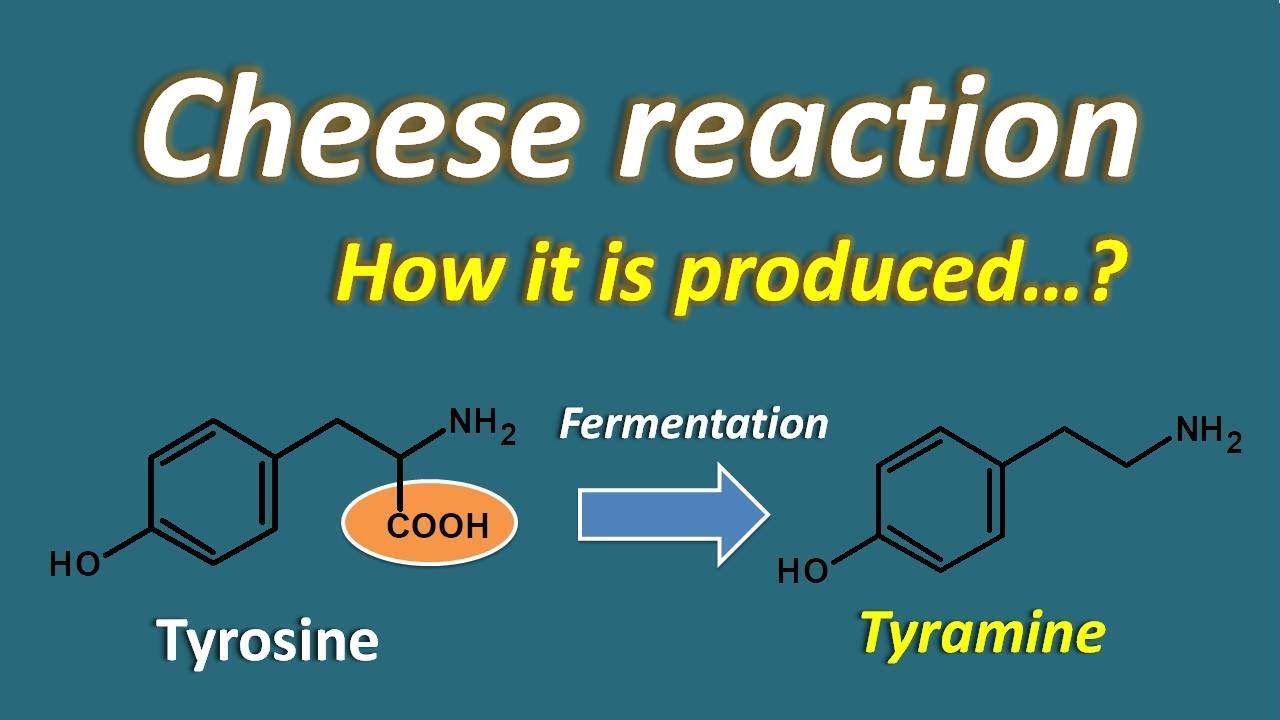


Cheese Reaction How It Is Produced Youtube



Maois Diet Full Amino Acid Foods



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Pdf Tyramine Potentiation During Treatment With Mao Inhibitors Brofaromine And Moclobemide Vs Irreversible Inhibitors



Awareness Of Interactions Has Come A Long Way Pharmacy Magazine



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿